What is a protein?
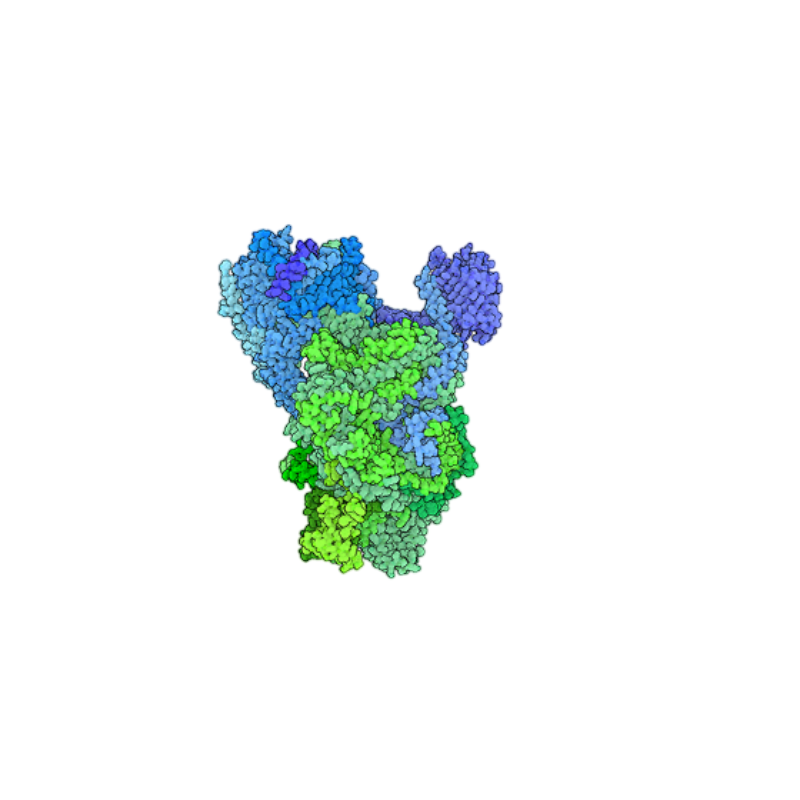
Structure
Proteins are large, complex molecules made of amino acid chains that fold into specific three-dimensional shapes. Their structure is critical because it determines how they function in essential biological processes like enzyme activity, cell signaling, and immune defense.

Clockwork
Learn more about biochemistry all around you with these stunning videos animations and inspiring voiceovers

Protein Data Bank
Explore the resources and educational materials of the Protein Data Bank, an organization that has been leading the community for decades.

TheBioCosmos
To learn more about the fundamental biology of proteins and cells you can check out the educational content from TheBioCosmos
LEARN
Common Questions
Why is protein structure important?
Structure determines function. The 3D shape of a protein dictates how it interacts with other molecules, enabling biological processes like catalysis (enzymes), signaling, or immune responses. Misfolded structures can lead to diseases like Alzheimer's or cystic fibrosis.
How do humans find protein structures?
- X-ray crystallography (high resolution but requires crystallization),
- NMR spectroscopy (good for small proteins in solution), and
- Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) (useful for large complexes).
- AI models like AlphaFold can predict structures computationally.
What are the four levels of protein structure?
- Primary: The linear sequence of amino acids.
- Secondary: Local folding patterns like alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
- Tertiary: The 3D structure of a single polypeptide chain.
- Quaternary: The arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains in a protein complex.
What makes up a protein?
Proteins are made of amino acids, which are organic molecules composed of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group (–NH₂), a carboxyl group (–COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group). A protein is formed when amino acids link together in a specific sequence via peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide chain.
Are the structures accurate?
The structures on FoldedThread are predicted protein structure from the AlphaFold Database is a 3D model of a protein generated using AI based on its amino acid sequence. While highly accurate, these models haven’t been proven by experimental methods like X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, or NMR spectroscopy.

